
Designed by Anmahian Winton Architects, this private astronomical observatory is located on a remote mountain summit in central New Hampshire. The site is characterized by granite outcroppings and is situated at the center of a three-mile radius “dark” landscape with very little light pollution to obstruct astronomical viewing. Instead of using a traditional dome, the design language features a synthesized architectural form that maximizes usable space and adapts to the geographic context. Discover the complete story after the jump.
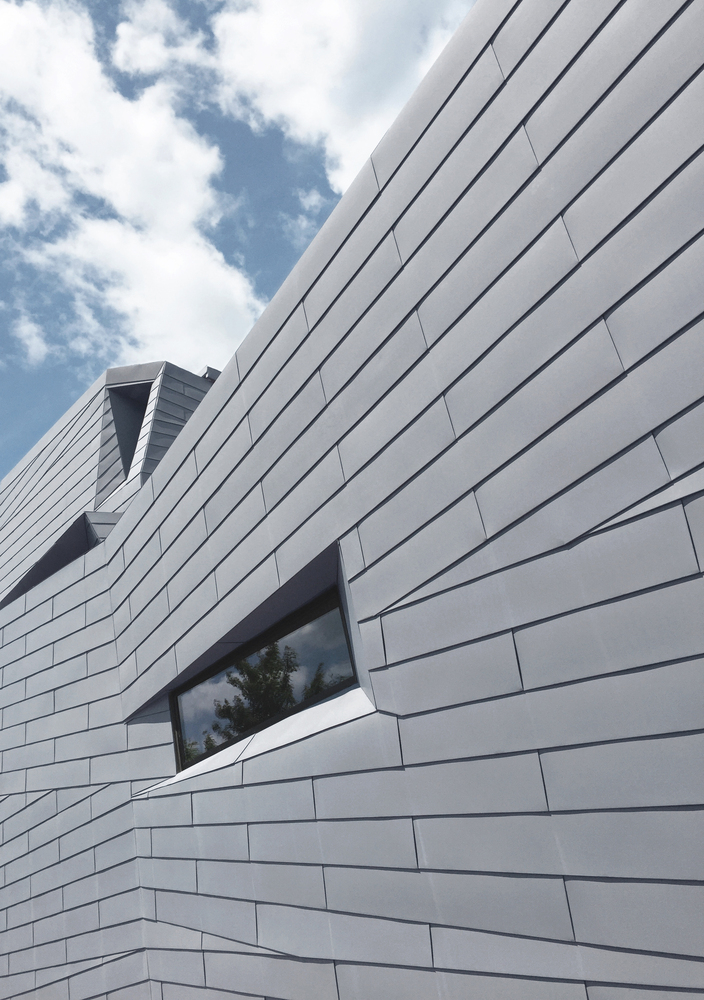
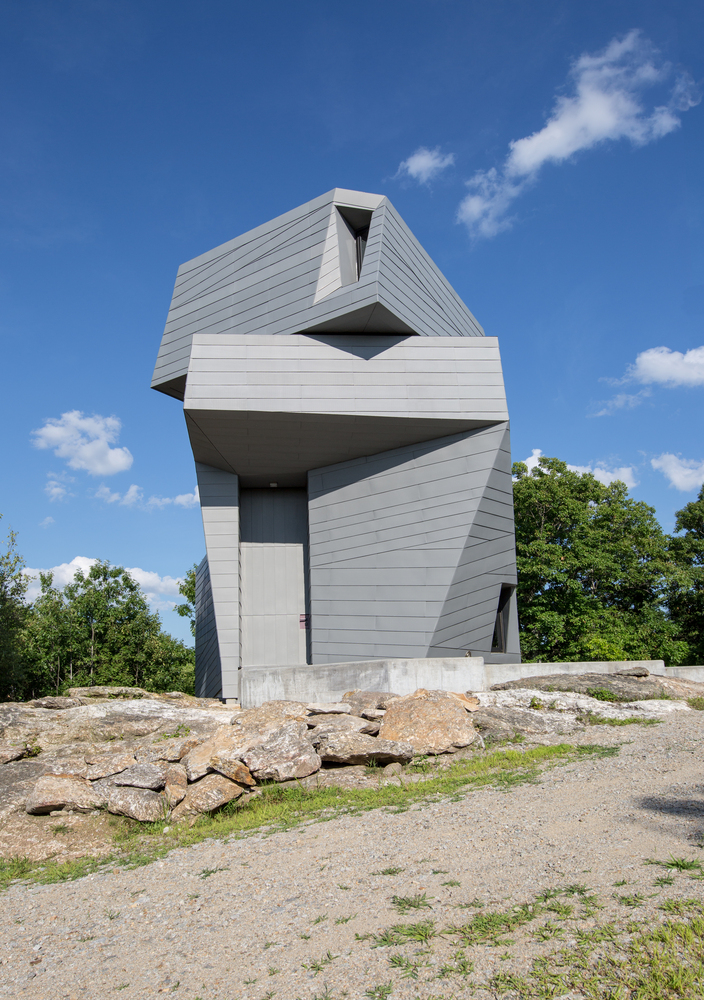
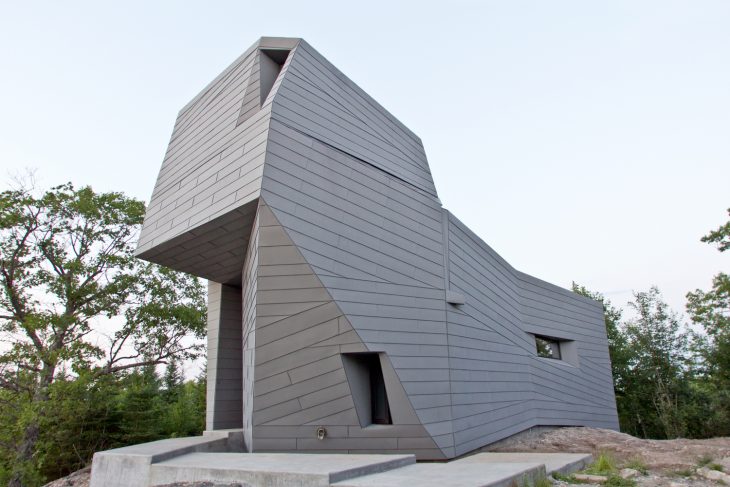
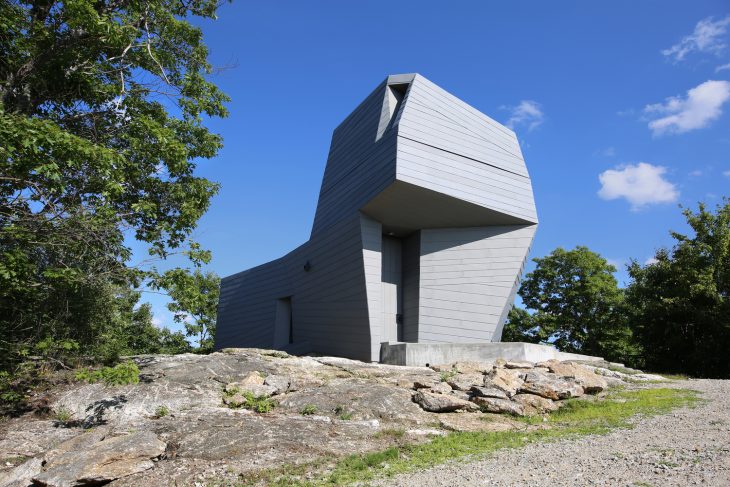













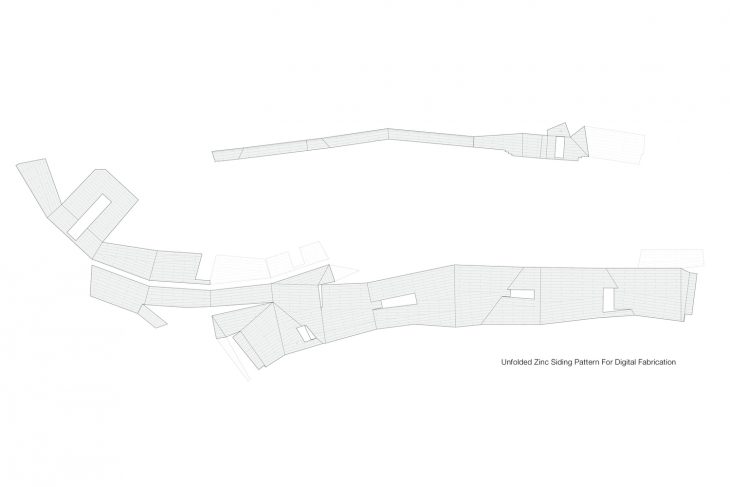
Gemma’s design rejects a traditional dome in favor of a synthesized architectural form that maximizes usable space and responds to the stark geographic context. Its continuously faceted shape reflects the surrounding landform, and terraced concrete platforms transition between the summit’s bedrock and the building foundation, knitting together natural and man-made landscapes. An unconventional pattern of lock-seamed zinc cladding mediates between the irregular site topography and the building’s geometry, reflecting Gemma’s orientation to both geological and celestial landmarks. Its dimension, color, and patina evoke a material relationship to the gray granite outcroppings, while its heat transfer capability facilitates sky observation by minimizing temperature differential distortion.
RELATED: FIND MORE IMPRESSIVE PROJECTS FROM THE UNITED STATES
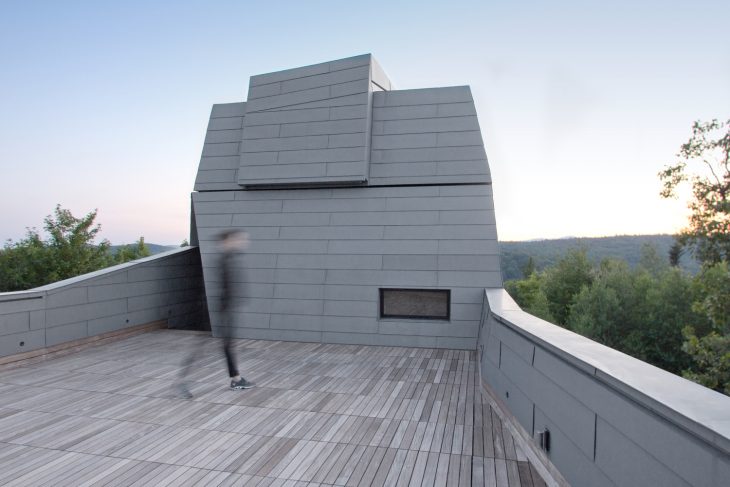
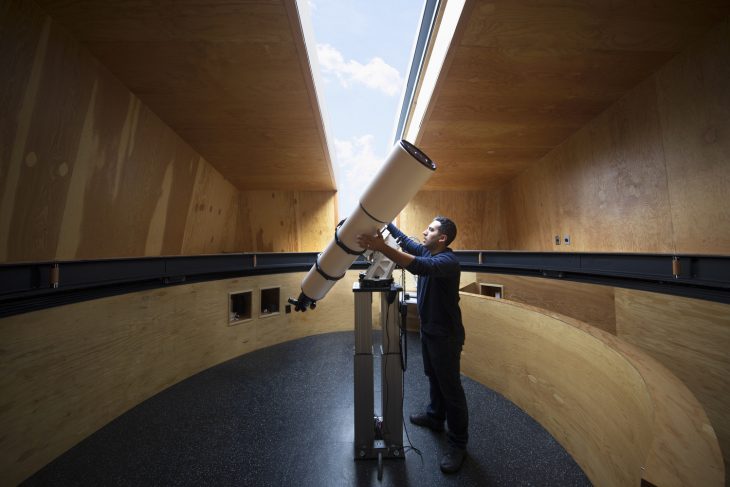
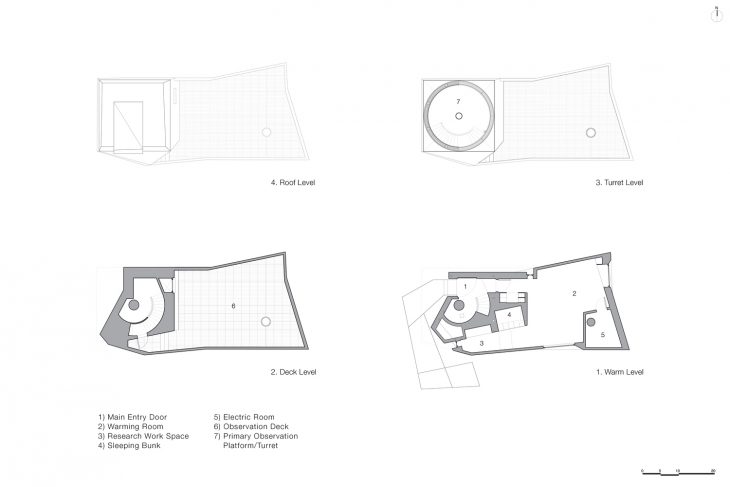
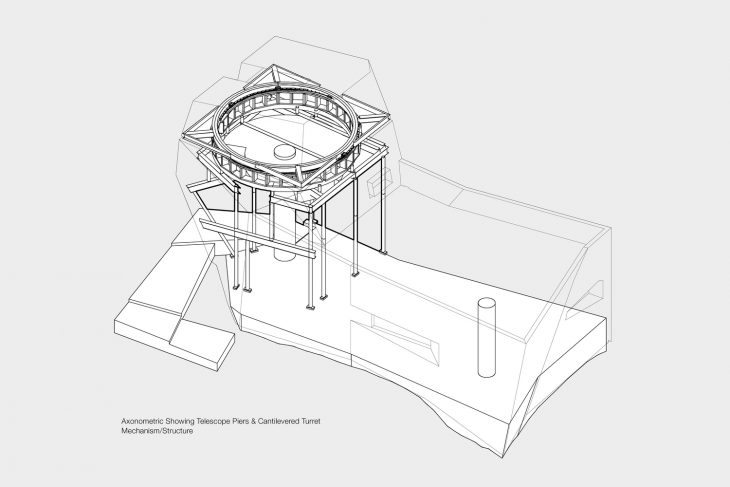
As a counterpoint to the exterior and its context, the interior is lined with fir plywood, creating a haven of refuge and warmth from the harsh surroundings. The first floor is comprised of a research office, sleeping bunk, and warming room, and is super-insulated to prevent interior/exterior temperature differentials from creating heat eddies that would impede astronomical viewing. A helical stair leads from the cantilevered entry canopy to a fissure in the cladding that opens onto the exterior observation deck. Continuing, the stair arrives at the observatory’s primary viewing platform inside the faceted turret, its interior characterized by high ceilings, a larger telescope, and a camera array. A single person can rotate this turret by hand with an assembly typically used in high-precision manufacturing facilities, and a hand-cranked sliding hatch opens the telescope to the sky. A rift in the zinc cladding creates a corner window, framing Polaris when the turret is locked into the southern cardinal position.
Images are Courtesy of Anmahian Winton Architects



